3.3. The Cluster Configuration Tool
Red Hat Cluster Manager consists of the following RPM packages:
clumanager — This package consists of the software that is responsible for cluster operation (including the cluster daemons).
redhat-config-cluster — This package contains the Cluster Configuration Tool and the Cluster Status Tool, which allow for the configuration of the cluster and the display of the current status of the cluster and its members and services.
You can use either of the following methods to access the Cluster Configuration Tool:
Select Main Menu => System Settings => Server Settings => Cluster.
At a shell prompt, type the redhat-config-cluster command.
The first time that the application is started, the Cluster Configuration Tool is displayed. After you complete the cluster configuration, the command starts the Cluster Status Tool by default. To access the Cluster Configuration Tool from the Cluster Status Tool, select Cluster => Configure.
The following tabbed sections are available within the Cluster Configuration Tool:
Members — Use this section to add members to the cluster and optionally configure a power controller connection for any given member.
Failover Domains — Use this section to establish one or more subsets of the cluster members for specifying which members are eligible to run a service in the event of a system failure. (Note that the use of failover domains is optional.)
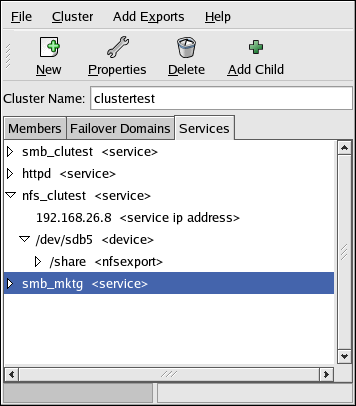
Services — Use this section to configure one or more services to be managed by the cluster. As you specify an application service, the relationship between the service and its IP address, device special file, mount point, and NFS exports is represented by a hierarchical structure. The parent-child relationships in the Cluster Configuration Tool reflect the organization of the service information in the /etc/cluster.xml file.

Warning Do not manually edit the contents of the /etc/cluster.xml file.
Do not simultaneously run the Cluster Configuration Tool on multiple members. (It is permissible to run the Cluster Status Tool on more than one member at a time.)
The Cluster Configuration Tool stores information about the cluster service and daemons, cluster members, and cluster services in the /etc/cluster.xml configuration file. The cluster configuration file is created the first time the Cluster Configuration Tool is started.
Save the configuration at any point (using File => Save) while running the Cluster Configuration Tool. When File => Quit is selected, it prompts you to save changes if any unsaved changes to the configuration are detected.
 | Note |
|---|---|
When you save the cluster configuration for the first time using the Cluster Configuration Tool and exit the application, the next time you the cluster (either by choosing Main Menu => System Settings => Server Settings => Cluster or by running redhat-config-cluster from a shell prompt) the Cluster Status Tool will display by default. The Cluster Status Tool displays the status of the cluster service, cluster members, and application services, and shows statistics concerning service operation. If you need to further configure the cluster system, choose Cluster => Configure from the Cluster Status Tool menu. The Cluster Configuration Tool) is used to configure cluster members, services, and cluster daemons. The Cluster Status Tool is used to monitor, start and stop the cluster members and services on particular members, and move an application service to another member. |
The Cluster Configuration Tool uses a hierarchical tree structure to show relationships between components in the cluster configuration. A triangular icon to the left of a component name indicates that the component has children. To expand or collapse the portion of the tree below a component, click the triangle icon.
To display the properties of a component, select the component and click Properties. As a shortcut, you can display the properties of a component by double-clicking on the component name.
To view or modify the properties of the cluster daemons, choose Cluster => Daemon Properties.